📘 LEVEL 1 — GLOBAL COMPLIANCE FOUNDATIONS
Goal:
Understand why compliance exists, global structure, regulatory bodies, and risk classification.
Covers:
- What is compliance?
- Hazard-based vs prescriptive standards
- Self-declaration vs mandatory approval
- Certification vs testing vs marking
- CB scheme
- Risk categories
1️⃣ What is Product Compliance?
Product compliance ensures that an electronic product:
- Is electrically safe
- Does not emit harmful interference
- Survives environmental stress
- Uses restricted materials properly
- Meets region-specific legal requirements
- Meets domain-specific risk requirements
Compliance = Technical conformity + Legal acceptance + Market access
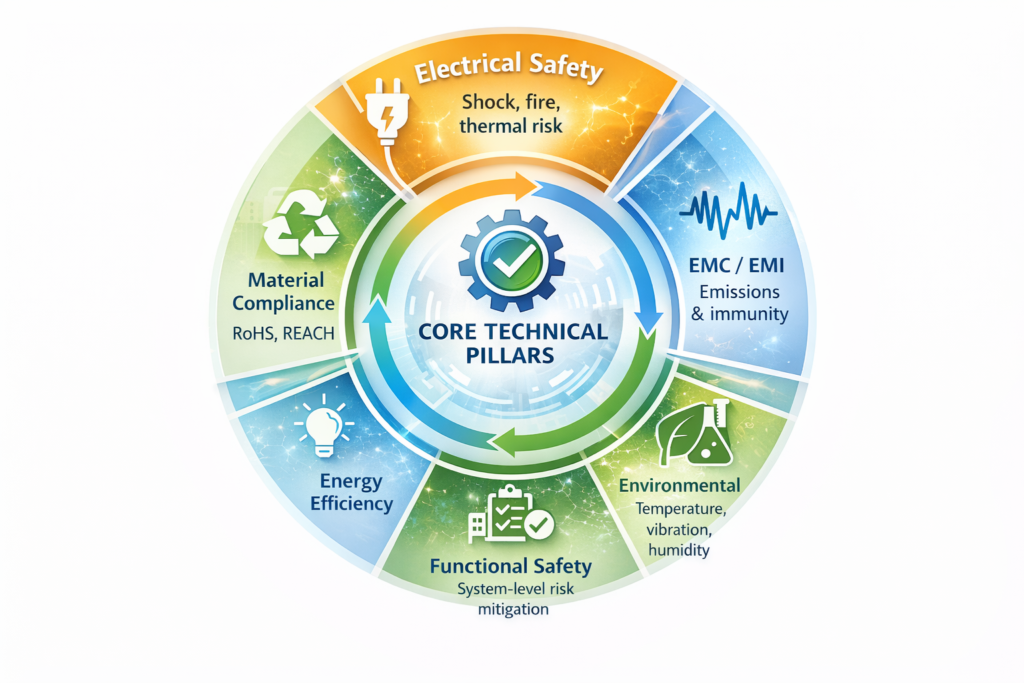
2️⃣ Global Compliance Structure (High-Level Model)
Every electronics product falls into these core pillars:
| Pillar | Covers |
|---|---|
| Electrical Safety | Shock, fire, thermal risk |
| EMC / EMI | Emissions & immunity |
| Environmental | Temperature, vibration, humidity |
| Functional Safety | System-level risk mitigation |
| Material Compliance | RoHS, REACH |
| Energy Efficiency | Power limits |
| Domain-Specific | Medical, automotive, etc. |
3️⃣ Global Regulatory Ecosystem
International Standards Bodies
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
These create standards.
Countries adopt or modify them.
4️⃣ Major Regional Regulatory Authorities
| Region | Authority | Mark |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | European Commission | CE |
| USA | Federal Communications Commission | FCC |
| USA | Underwriters Laboratories | UL |
| China | China Compulsory Certification | CCC |
| India | Bureau of Indian Standards | BIS |
| Japan | METI | PSE |
| Korea | KATS | KC |
| Australia | ERAC | RCM |
5️⃣ Domain Overview — Standards Listing (High-Level)
Now we list standards domain-wise (no deep explanation yet).
🏠 A) Consumer Electronics
Electrical Safety
- IEC 62368-1
- IEC 60335 (Household appliances)
EMC
- CISPR 32
- CISPR 35
- IEC 61000-4-x series
Environmental
- IEC 60068 series
Material
- RoHS
- REACH
- WEEE
🚗 B) Automotive Electronics
Electrical & Environmental
- ISO 16750
- ISO 7637 (transients)
EMC
- CISPR 25
- ISO 11452
Functional Safety
- ISO 26262
Component Qualification
- AEC-Q100 / Q200
🏭 C) Industrial Equipment
Safety
- IEC 61010-1
- IEC 60204 (Machinery electrical safety)
EMC
- IEC 61000-6-2 (Industrial immunity)
- IEC 61000-6-4 (Industrial emission)
Environmental
- IEC 60068
- IP ratings (IEC 60529)
🏥 D) Medical Devices
Electrical Safety
- IEC 60601-1
EMC
- IEC 60601-1-2
Risk Management
- ISO 14971
QMS
- ISO 13485
✈️ E) Aerospace
Environmental
- RTCA DO-160
EMC
- DO-160 Section 20
Quality
- AS9100
🛡 F) Defence
EMC
- MIL-STD-461
Environmental
- MIL-STD-810
Quality
- MIL-STD-883 (microelectronics)
🚢 G) Marine / Naval
Safety & Environmental
- IEC 60945
Classification Bodies
- DNV rules
- Lloyd’s Register
6️⃣ Certification Types (Cross-Domain)
| Type | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Self-Declaration | Manufacturer declares compliance |
| Third-Party Certification | Accredited lab approval |
| Type Approval | Government certification |
| CB Scheme | International safety report sharing |
7️⃣ Hazard-Based vs Prescriptive Standards
Modern standards (IEC 62368) → Hazard-based
Older standards → Construction-based
This is important for future deep learning.
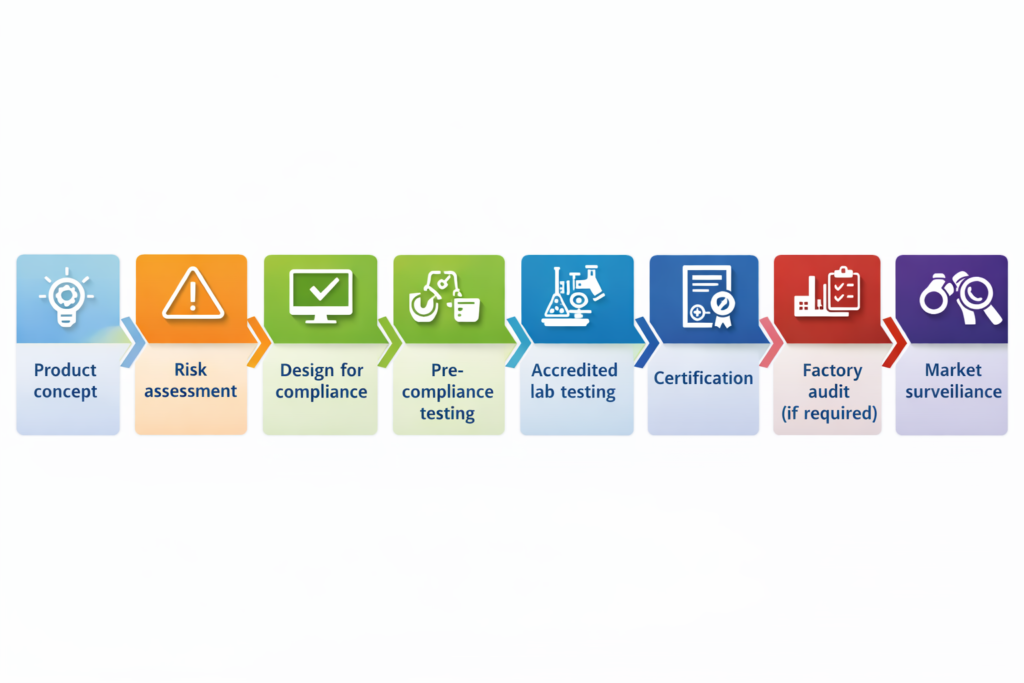
8️⃣ Compliance Lifecycle
- Product concept
- Risk assessment
- Design for compliance
- Pre-compliance testing
- Accredited lab testing
- Certification
- Factory audit (if required)
- Market surveillance
🎯 Outcome of Level 1
After Level 1, an engineer should:
- Understand all major domains
- Recognize key standards per domain
- Know which pillar applies to which product
- Understand regulatory vs voluntary marks





Leave a Reply